What is EQE?
Event-Centric Query Expansion (EQE) is a real-time and efficient query expansion framework designed for timely search scenarios. It is proposed by researchers from Tencent QQ Browser Search and deployed in a real production environment.
For more details, please refer to our ACL 2023 Industry Track paper:
(Zhang2023EventCentricQE)
One More Thing
We disclose an annotated test
dataset for Event Reformulation, which is called Title2EventPhrase.
This open dataset features a large-scale collection of human-annotated Chinese titles and includes
41,000 <headline, event> pairs.
Further details can be found at
Citation
If you find this project helpful to your research or use the code or data from this project, please cite our paper.
@inproceedings{zhang-etal-2023-event,
title = "Event-Centric Query Expansion in Web Search",
author = "Zhang, Yanan and
Cui, Weijie and
Zhang, Yangfan and
Bai, Xiaoling and
Zhang, Zhe and
Ma, Jin and
Chen, Xiang and
Zhou, Tianhua",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 5: Industry Track)",
month = jul,
year = "2023",
address = "Toronto, Canada",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2023.acl-industry.45",
pages = "464--475",
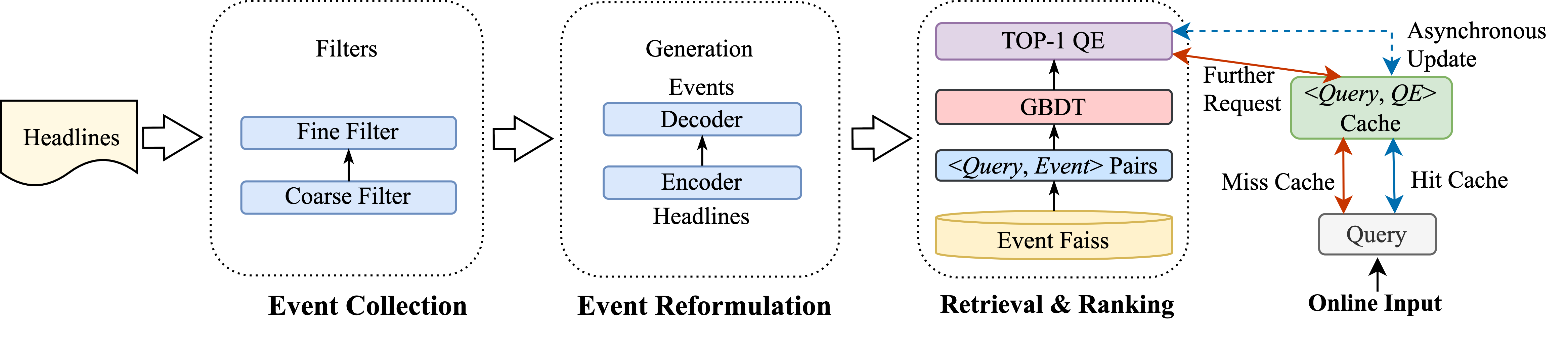
abstract = "In search engines, query expansion (QE) is a crucial technique to improve search experience. Previous studies often rely on long-term search log mining, which leads to slow updates and is sub-optimal for time-sensitive news searches. In this work, we present Event-Centric Query Expansion (EQE), the QE system used in a famous Chinese search engine. EQE utilizes a novel event retrieval framework that consists of four stages, i.e., event collection, event reformulation, semantic retrieval and online ranking, which can select the best expansion from a significant amount of potential events rapidly and accurately. Specifically, we first collect and filter news headlines from websites. Then we propose a generation model that incorporates contrastive learning and prompt-tuning techniques to reformulate these headlines to concise candidates. Additionally, we fine-tune a dual-tower semantic model to serve as an encoder for event retrieval and explore a two-stage contrastive training approach to enhance the accuracy of event retrieval. Finally, we rank the retrieved events and select the optimal one as QE, which is then used to improve the retrieval of event-related documents. Through offline analysis and online A/B testing, we observed that the EQE system has significantly improved many indicators compared to the baseline. The system has been deployed in a real production environment and serves hundreds of millions of users.",
}